~ 2 min read
npm security tips to keep you safe of malicious modules

Tip 3: Minimize attack surfaces by ignoring run-scripts (out of 10 npm security best practices)
The npm CLI works with package run-scripts. If you’ve ever run npm start or npm test then you’ve used package run-scripts too.
The npm CLI builds on scripts that a package can declare, and allows packages to define scripts to run at specific entry points during the package’s installation in a project.
For example, some of these script hook entries may be postinstall scripts that a package that is being installed will execute in order to perform housekeeping chores.
With this capability, bad actors may create or alter packages to perform malicious acts by running any arbitrary command when their package is installed.
A couple of cases where we’ve seen this already happening is the popular eslint-scope incident that harvested npm tokens, and the crossenv incident, along with 36 other packages that abused a typosquatting attack on the npm registry.
Apply these best practices in order to minimize the malicious module attack surface:
-
Always vet and perform due-diligence on third-party modules that you install in order to confirm their health and credibility.
-
Hold-off on upgrading blindly to new versions; allow new package versions some time to circulate before trying them out.
-
Before upgrading, make sure to review changelog and release notes for the upgraded version.
-
When installing packages make sure to add the
--ignore-scriptssuffix to disable the execution of any scripts by third-party packages. -
Consider adding
ignore-scriptsto your.npmrcproject file, or to your global npm configuration.
—
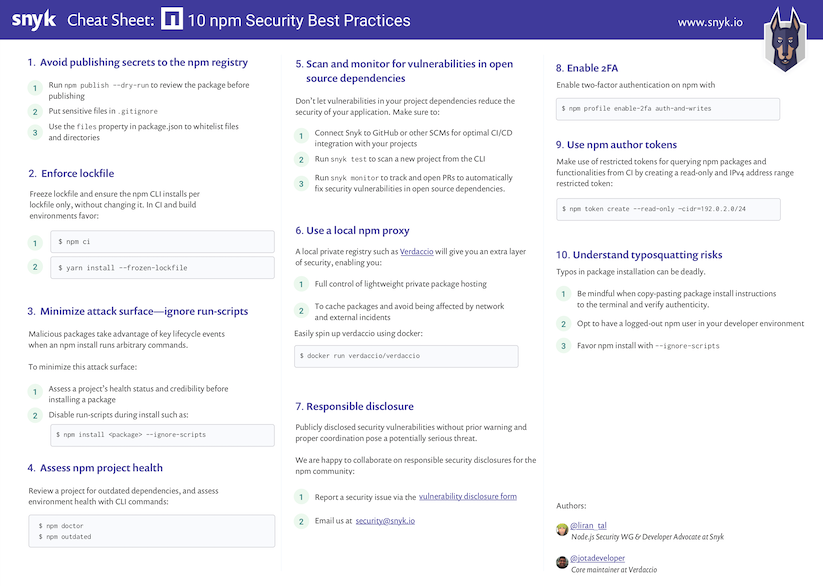
I also blogged about a complete 10 npm security best practices you should adopt in a post that includes a high-resolution printable PDF like the snippet you see below.
Thanks for reading and to Juan Picado from the Verdaccio team who worked with me on it.